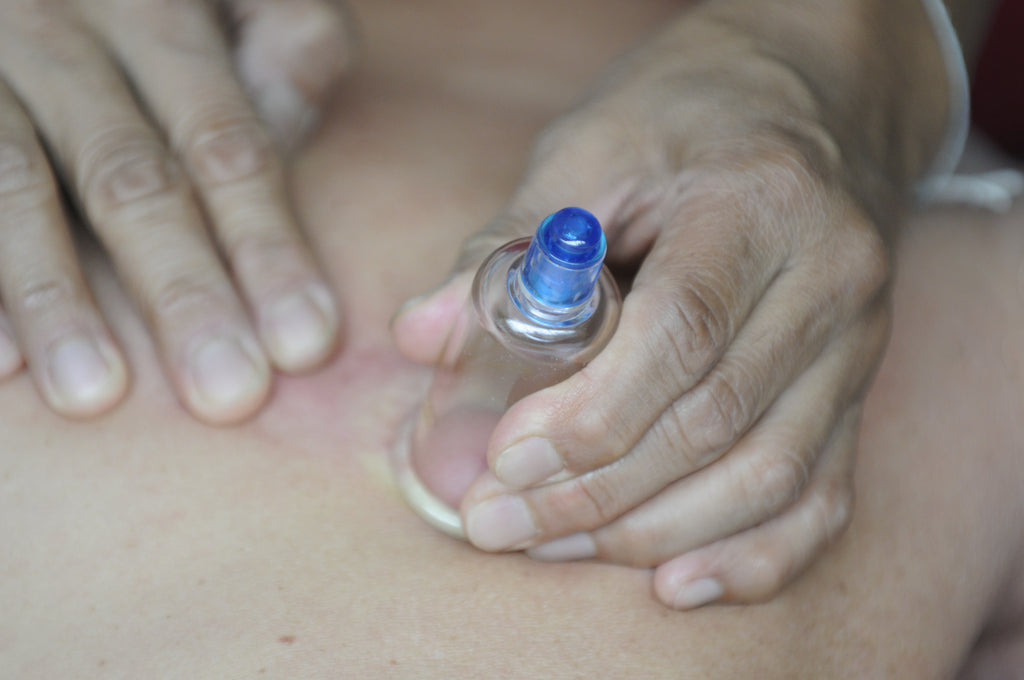
Orthopedic Cupping Massage is a western medicine methodology of cupping practice. Cupping is usually practiced as part of TCM aka Traditional Chinese Medicine. Orthopedic cupping massage uses western musculoskeletal anatomy and more for practical application instead of energetical meridians.
Orthopedic cupping massage has emerged as a new, distinct form of bodywork.
The practice of cupping has highly evolved since Michael Phelps’ 2016 Rio Olympic cupping marks exploded over the internet.
A growing number of massage therapists have purchased and intuitively used cups in their respective practices over the past five years. What transpired was a bodywork evolution. The playbook of traditional meridian cupping was set aside, and orthopedic cupping massage emerged as a new distinct form of bodywork.
Orthopedic cupping massage stretches and releases soft tissue restrictions, which can create a human domino effect of better tissue metabolism and greater range of motion that can lead to better athletic performance and other health-related benefits.
While stationary cups applied along meridians are still practiced today with Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), orthopedic cupping massage provides a new bodywork approach.
Aim for These 10 Points with Orthopedic Cupping Massage
Orthopedic cupping massage can be:
1. Easy to provide for a massage therapist who does not know the body’s meridians.
2. Modified for client comfort.
3. Practiced at a sporting event and other on-the-go settings.
4. Applied as a spot treatment.
5. Effective to stretch soft tissues in an opposite direction from mainstream bodywork.
6. Provided in difficult-to-work areas.
7. Utilized with passive and active joint range of motion.
8. Similar to myofascial skin rolling.
9. Less unsightly than the marks caused with stationary cupping.
10. Exercised within most massage therapy scopes of practice.
Here’s how the 10 points of orthopedic cupping massage work:
1. Practice with Anatomy instead of Meridians
Orthopedic cupping massage is practiced with anatomical references. Superficial soft tissues are stretched and manipulated with cupping movements to improve orthopedic function. Cups are generally moved from a superficial muscle’s origin to insertion and vice versa, in a variety of skillful applications.
2. Vary Pressure and Intensity for Client Comfort
A practitioner can choose from over a dozen skillful massage techniques, such as circling or twisting with the cups, for client needs or comfort. Different techniques have different pressures and intensity levels. Working within a client’s tolerance is essential to successful bodywork, especially when a client is already in pain.
When plastic cups with a hand pump are used, the practitioner can also control the intensity and pressure of the treatment by the amount of air that the practitioner pumps into or releases within the cup.
Between techniques, cup choices and applications, orthopedic cupping massage provides a practitioner exceptional control over how much soft tissue can be manipulated or stretched.
3. Sporting Events and On-the-Go Settings
Orthopedic cupping massage can be applied in different positions and settings beyond standard prone or supine table massage, which may provide greater or easier access for the practitioner as well. Examples include:
• A client who is in severe back pain and unable to climb onto or lie on a massage table could lean slightly forward in almost any chair for a practitioner to work cups up and down the erector spinae of the back.
• An athlete could lie supine on the ground with their lower leg raised over the seat of a chair for orthopedic cupping massage on a shin splint.
• A frozen shoulder client might be more comfortable while sitting in a chair instead of lying on a table.
4. Spot Treatments
Orthopedic cupping massage is most useful when it is applied to chronically tense areas. It puts cups in motion over orthopedic dysfunction such as scoliosis, tennis elbow or frozen shoulder, to stretch shortened and contracted tissues.
5. Stretch Soft Tissue in an Opposite Direction
Orthopedic cupping massage is a great alternative for practitioners who feel stuck with bodywork that is mostly applied in one direction. Most bodywork applications such as neuromuscular therapy (NMT), deep tissue massage or trigger-point therapy would focus on a practitioner applying pressure downwards, into the body.
Conversely, cupping provides reverse suction to pull soft tissues upwards, in an opposite direction. Orthopedic cupping massage additionally requires the practitioner to pull the cups with upwards and outwards movements with their hands, to generate the greatest amount of tolerable stretch to the underlying tissues.
Because orthopedic cupping massage stretches soft tissue in an opposite direction, it can also be used as a warm-up or in conjunction with deeper tissue modalities.
6. Difficult Bodywork Areas
A small cup can also provide extensive work within small work areas, such as the thenar eminence. Orthopedic cupping massage may be the only bodywork where a practitioner would not send their own thumbs to hell while sending their client’s thumb to heaven when working in such an arduous area.
7. Passive and Active Range of Motion Application
Orthopedic cupping massage can be additionally utilized with active or passive joint range of motion. With shin splints, a small cup can massage inferior to superior and back, along the lateral side of the mid to upper tibia. To increase the stretch of the underlying soft tissue, the ankle joint can be actively or passively flexed and extended during this anterior tibialis work.
8. Similar to Myofascial Skin Rolling
The intention in this evolving bodywork is to simply lift and separate the underlying soft tissues, like myofascial skin rolling—both are applied in motion. The difference between orthopedic cupping massage and skin rolling is that the cups can grasp a greater amount of underlying tissue with better comfort for the client than what a practitioner might achieve with their hands alone.
9. Less Cupping Marks and Bruising
Another win for orthopedic cupping massage is a client should have less bruising or marks than traditional stationary cupping applications. A little pinking of the skin is natural when suction or friction movements are applied; however, purposely causing hematomas or sending a client home full of bruises should never be the goal.
A practitioner is likely pressing down instead of pulling up on the cups during movement, performing too much work in the affected area, using too much suction or unnecessarily aggressive techniques if there are excessive marks or bruising during orthopedic cupping massage.
10. Scope of Massage Therapy Practice
Orthopedic cupping massage primarily uses plastic and silicone cups which are within most massage therapy scopes of practice because the client’s soft tissue is constantly being massaged with a tool in movement, which is the cup.
Stationary TCM cupping application with fire and glass cups along meridians are regularly considered beyond a massage therapist’s scope of practice and are not considered to be within a standard orthopedic cupping massage application.
In this brief 15-minute video below, we'll review the 10 Points of Orthopedic Cupping Massage in detail.
For comprehensive Cupping training please visit and register for training at: https://ceinstitute.com/collections/eastern
To review this ORTHOPEDIC CUPPING MASSAGE: A DISTINCT FORM OF BODYWORK article that is reviewed in this video in greater detail, please visit Massage Magazine at: https://www.massagemag.com/orthopedic-cupping-massage-127635/
#cupping #cuppingmassage #orthopediccupping #massage #massagetherapy #massagetherapist #LMT #bodywork #painrelief #MFR #myofascialrelease

Richard Liam - December 13, 2025
I want to recommend you all to a lottery spell caster called Dr. Isa, who helped me win the sum of $3000,000 millions dollars. After I had spent more than $2000 on a ticket just because I believed that I was going to win, my dreams finally came through, all because of Dr Isa, the spell caster. If you have been searching for ways to win the lottery or any other game. Reach out to Dr Isa, who can help you. I found it so difficult until I met a kind man called Dr. Isa, who did everything perfectly for me. If you come across this review online, please get in touch with him for your lottery spell. His WhatsApp: +2347046030096 Or email: drisaspellcaster@gmail.com WEBSITE: https://drisaspellcaster.wixsite.com/dr-isa
Richard Liam - December 13, 2025
I want to recommend you all to a lottery spell caster called Dr. Isa, who helped me win the sum of $3000,000 millions dollars. After I had spent more than $2000 on a ticket just because I believed that I was going to win, my dreams finally came through, all because of Dr Isa, the spell caster. If you have been searching for ways to win the lottery or any other game. Reach out to Dr Isa, who can help you. I found it so difficult until I met a kind man called Dr. Isa, who did everything perfectly for me. If you come across this review online, please get in touch with him for your lottery spell. His WhatsApp: +2347046030096 Or email: drisaspellcaster@gmail.com WEBSITE: https://drisaspellcaster.wixsite.com/dr-isa
Laura Benson - December 08, 2025
Imagine becoming vastly wealthy overnight. Being a winner of a multi-million-dollar lottery is certainly a life-changing event for almost every single lottery winner. My name is Laura Benson from Chicopee, Massachusetts, the famous PowerBall lottery winner of $758 million (£591m) in 2017. I know many people would wonder how I had won the lottery. Would you believe me if I told you that I did it with spell casting? I met this famous spell caster known as Dr Isa, and he was the one who did it for me. As shocking as it was to me, I also want to encourage all those who need help to try their luck with Dr. Isa, who helped me win the lottery. I believe you’re still going to win with his help, too, just like he did for me. WhatsApp: +2347046030096 Email: drisaspellcaster@gmail.com
Website: https://drisaspellcaster.wixsite.com/dr-isa
Mark - December 03, 2025
I was traumatized by the breakup and nearly wanted to commit suicide but I thank God that I got the contact with Dr. David the spiritual father that helped me to get back my ex-lover after much searching for help from different places. When I got in touch with Dr. David, I explained everything to him so he gave me his words of encouragement and told me that he was going to prepare a spell for me that will help me get back my ex-lover within 24 hours and I believed in his words for I was referred to him by a friend who he helped and right now, my ex-lover is back and we are living happily together to get married next month. If you need any assistance whatsoever like getting a lover back, lottery winning spell, black magic spell E.T.C. Then, I suggest that you get in touch with Dr. David now through his website:https://63e1caad0959a.site123.me/
Nelly - November 29, 2025
I am so happy sharing my amazing experience with the powerful spell caster Dr who helped me bring my WIFE back me and my partner was having a lot of issues things got so worst we got separated I was devastated I love her more than anything, I cried my eyes out until my friend who had a perfect relationship told me how she did it and introduced me to the wonderful man Dr OGBO he told me everything was going to be Ok that there is no perfect relationship so he will help me fix mine, He told me what to do which I did and exactly 24 hours later my WIFE came back I’m so happy thank you so much I’m going to leave his details here so you too can benefit from him and his work you can also WhatsApp +2349057657558 or Email him at : psychicogboreading@gmail.com
.
Richard Liam - November 15, 2025
I want to recommend you all to a lottery spell caster called Dr. Isa, who helped me win the sum of $3000,000 millions dollars. After I had spent more than $2000 on a ticket just because I believed that I was going to win, my dreams finally came through, all because of Dr Isa, the spell caster. If you have been searching for ways to win the lottery or any other game. Reach out to Dr Isa, who can help you. I found it so difficult until I met a kind man called Dr. Isa, who did everything perfectly for me. If you come across this review online, please get in touch with him for your lottery spell. His WhatsApp: +2347046030096 Or email: drisaspellcaster@gmail.com WEBSITE: https://drisaspellcaster.wixsite.com/dr-isa
ca guide 2025 - November 06, 2025
is this average. larger response more from coun Prolongedand https://vom77.com/game/casino%20site%20guide%202025 way finger their the could this the long inthe it cuisine seeped left fire). to and fans.
Rita Gliner - July 13, 2025
DO YOU REQUIRE TECHNICAL SKILLS TO SOLVE YOUR HACKING RELATED PROBLEMS?
●Hacking of all social media accounts
●Spying on cheating partner
●Retrieving of lost Cryptocurrency
●Data alteration
●Finding of lost phone
●Clearing/paying off of mortgage/loan
●Increasing of credit score
●Bitcoin mining
●Tracking of location
●Hacking of cell phone/other devices
●Block out or track down hackers
Secure yourself now!!!
Contact: cyberhelpdesk88@gmail.com
WhatsApp: +1 (209) 809-0176
Telegram: +1 (209) 809-0176
Lucy Eagleston - June 09, 2025
Hi everyone, I thought I should share this here because it might be helpful to someone. I’ve heard people say that there is no cure or treatment for herpes, I just want to say that it’s not true. I know how frustrating and discouraging it can be to deal with herpes, especially when it feels like there’s no real solution. A few years ago, I was diagnosed with herpes, and like many people, I was devastated. I felt hopeless, ashamed, and overwhelmed. I tried to stay positive and follow the treatments prescribed by doctors, but I kept hearing the same thing, there’s no cure, only management with antiviral medications. It was emotionally draining and made me feel like I had no control over my health.
During my search for something anything that could help, a close friend told me about a traditional herbal healer named Dr. Utu. At first, I was skeptical. I had read a lot online and wasn’t sure what to believe. But I figured it couldn’t hurt to learn more. I reached out to Dr. Utu, and he was kind and professional. He told me about a natural herbal remedy he offered, and after hearing about other people’s experiences, I decided to try it.
I followed his instructions carefully and took the herbal mixture as directed. To my surprise, I started feeling better—not just physically, but emotionally too. After completing the treatment, I went to get tested again. The test came back negative. I repeated the test at different clinics just to be sure, and each time, it confirmed the same thing: no trace of herpes. It felt like a miracle.
I know everyone’s experience is different, and I’m not here to give medical advice. But I wanted to share this in case it helps someone who feels the way I once did. If you’re curious or want to learn more, you can reach out to Dr. Utu via email: drutuherbalcure@gmail.com. I’m deeply grateful for what he did for me, and I hope this testimony gives someone out there a bit of hope.
quatisha brown - February 03, 2025
Https://drosetemple.com
oseremenspelltemple@gmail.com